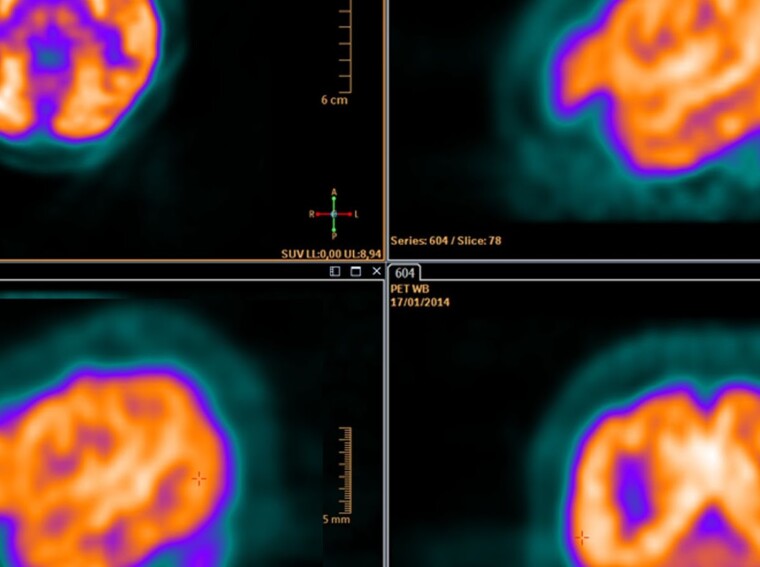
PET scans are an essential diagnostic tool used to detect cancer in patients. By tracking the uptake of a radiotracer, PET can produce detailed images of metabolic activity within the body. These images allow for early detection and accurate staging of tumours, as well as monitoring cancer treatment effectiveness.
During a PET or Craft Body Scan, the patient is injected with a small amount of radioactive material that then accumulates in areas with high metabolic activity such as cancer cells. Then, a specialised camera detects and records the energy emitted by the radiotracer, producing detailed images that can be analysed by medical professionals.
PET scans have many benefits over other imaging techniques; they are noninvasive, produce more accurate results than some other techniques, and provide a visual representation of metabolic activity within the body. It also allows doctors to identify abnormal growths even before they become large enough to trigger symptoms.
Don’t wait until it’s too late- get ahead of cancer with the help of PET scans. Talk to your doctor today about how this technology can help detect and monitor cancers earlier.
Using PET scans to detect cancer is like playing hide and seek with the deadliest of opponents; fortunately, we have a few tricks up our sleeve.
Importance of PET Scans in Cancer Detection
To understand the significance of PET scans in detecting cancer, look for how PET scans work and the benefits they offer. If you are wondering how PET scans work, or what the advantages of PET scans for cancer detection are, we have got you covered.
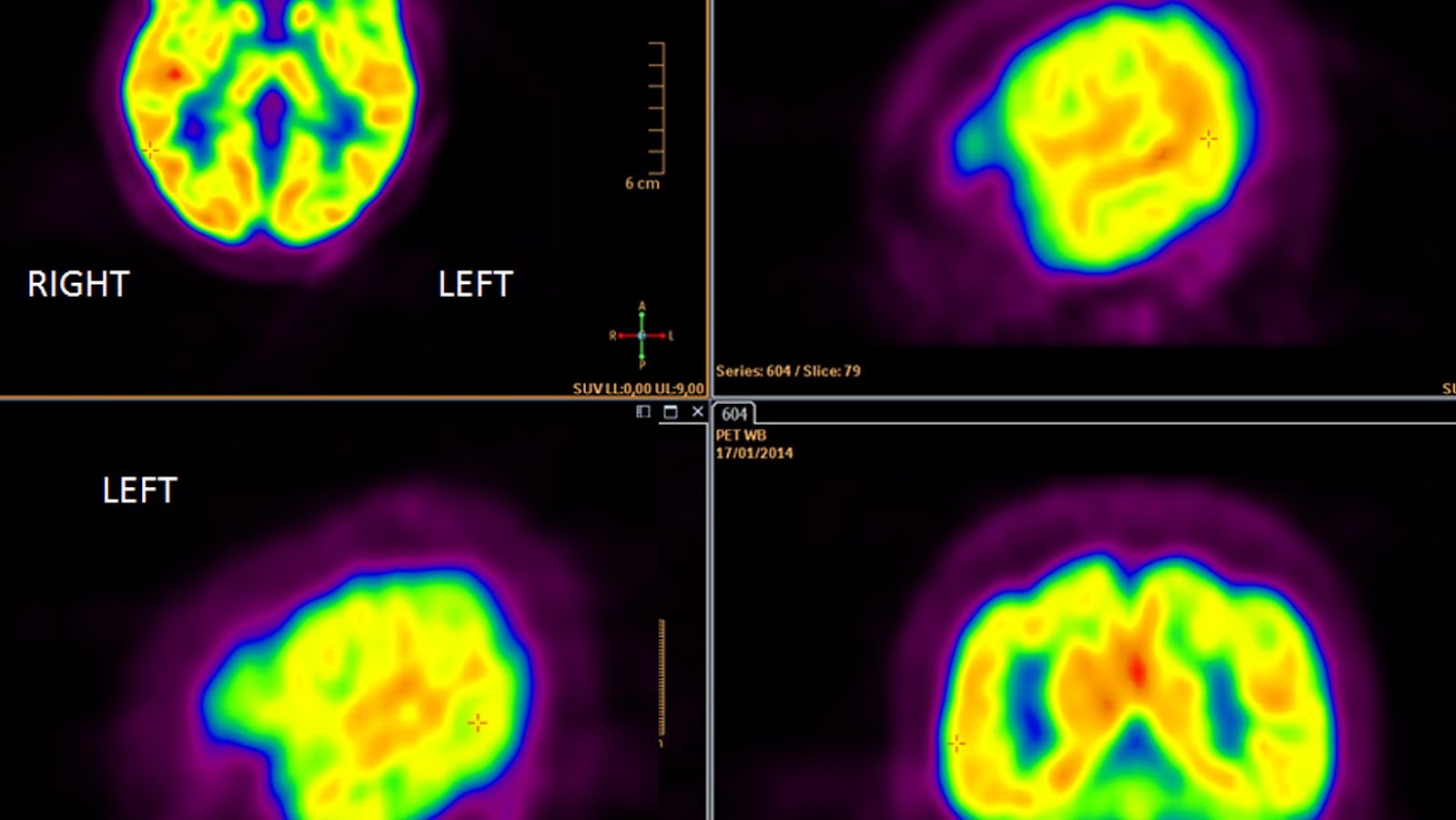
How PET Scans Work
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans work by using a small amount of radioactive tracer, which is injected into the patient’s bloodstream. This tracer then attaches itself to glucose, and as cancerous cells consume more glucose than healthy cells, the PET scan can detect areas with increased metabolic activity. The scanner detects gamma rays emitted from the tracer in the body and constructs images of the area with increased activity.
PET scans are useful in detecting cancerous tumours and identifying their stage, as well as determining if the cancer has metastasized to other areas of the body. By providing highly detailed images of a patient’s internal organs and tissues, PET scans can help doctors differentiate between benign growths and malignant tumours. These detailed images can also be used to monitor how well certain treatments are working, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
It is worth noting that PET scans do have some limitations; they cannot diagnose all types of cancer, and sometimes they produce false-negative or false-positive results. Additionally, because the radioactive tracer used can expose patients to a small amount of radiation, certain patients may not be able to undergo repeated PET scans.
A pivotal moment came when researchers at Washington University in St. Louis discovered that they could use PET imaging to facilitate early detection of Alzheimer’s disease by identifying changes in brain metabolism before significant neuronal damage occurs (a common feature of AD). They observed that the same protein clumps found in AD (beta-amyloid) trigger inflammatory responses that disrupt blood flow regulation in older people even before evidence of cognitive decline appears, paving way for early diagnosis through PET imaging.
Why settle for a basic X-ray when a PET scan can give you a full-body selfie with cancer detection?
Advantages of PET Scans for Cancer Detection
The usage of PET scans in the detection of cancer is highly beneficial. The benefits of PET scans go beyond what regular imaging tests can provide and aid in life-saving diagnosis.
The following are the benefits of PET scans:
- PET scans detect cancer early, making it easier to start treatment at an early stage.
- They aid in determining the extent of cancer within the body.
- PET scans differentiate between malignant tumours and benign lesions, making it easier for doctors to determine a course of treatment.
- They pinpoint tumours that are difficult to detect by other imaging procedures like CT or MRI Scans, leading to accurate diagnoses.
- They allow physicians to monitor patient response to chemotherapy and other treatments as they observe how tumours change with each scan.
- PET scans demonstrate excellent specificity and sensitivity when detecting cancer cells in the body.
PET scans provide exceptional assistance throughout cancer diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, these images reveal more information than any other diagnostic test.
A recent study published by the American Cancer Society revealed how using PET imaging along with conventional breast imaging techniques helped identify nearly one-third more invasive cancers compared to those who utilised traditional methods alone. Finally, a way to see inside your body without resorting to extreme measures like X-ray vision or becoming a superhero.
If Pet Scan is Positive Can it be Anything But Cancer
To understand PET scan results and cancer diagnosis with interpreting PET scan results and whether a positive PET scan can be anything but cancer, read on.
Interpreting PET Scan Results
PET scans provide valuable insight into cancer diagnosis by detecting metabolic activity. Physicians analyse PET scan results to identify areas with increased metabolic activity. Elevated activity in an area may indicate cancer or inflammation, leading to further testing and diagnoses. PET scans can also help determine the stage and severity of cancer, which guides treatment options. It is important to discuss PET scan findings with a qualified healthcare professional for accurate interpretation and appropriate action.
Well, a positive PET scan result could mean you’re just a hot and spicy individual, but let’s not rule out cancer just yet.
Can a Positive PET Scan Result be Anything But Cancer?
A PET scan provides information on how body tissues and organs work, such as blood flow or metabolism. However, a positive result on a PET scan may not always indicate cancer. In some cases, it could be due to other conditions such as infections or inflammation.
In addition to cancer, a PET scan result can suggest several other diseases including heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease or Parkinson’s disease. It is important to consult with your healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment plan.
Furthermore, limiting physical activity before the PET scan and drinking plenty of water after the test can improve the accuracy of the results. Additionally, preparing for the scan by following specific instructions from your doctor would help in obtaining more reliable results.
Overall, while a positive PET scan result could be due to various reasons aside from cancer, it is crucial to discuss the results with your physician. They can determine the cause behind the abnormality and establish an effective course of treatment that complements your overall health needs.
Looks like my PET scan is showing potential signs of nothing-but-hypochondria syndrome.
Other Conditions that may Affect PET Scan Results
To identify other possible conditions that could affect PET Scan results, this section explores the link between Inflammatory Diseases, Infections, and PET Scan Results. By understanding how these factors can impact PET Scan results, you can gain a better understanding of the limitations of PET Scans for cancer detection. We will examine the sub-sections: Inflammatory Diseases and PET Scan Results, Infections and PET Scan Results, providing an overview of how they can affect the accuracy of PET Scans.
Inflammatory Diseases and PET Scan Results
PET scans are medical imaging tests that use radioactive material to detect and measure different bodily functions. Inflammatory diseases such as arthritis, lupus, and vasculitis can affect PET scan results by causing areas of inflammation that may be mistaken for cancer. This can lead to false-positive results and unnecessary further testing.
It is important for patients with inflammatory diseases to inform their healthcare providers about their condition before undergoing a PET scan. In some cases, medication used to manage these conditions may also affect the accuracy of PET scans. Additionally, certain infectious diseases such as HIV and tuberculosis can also cause false-positive results and should be disclosed to healthcare providers beforehand.
Pro Tip: It is crucial for patients with inflammatory or infectious diseases to discuss their condition with their healthcare provider before undergoing a PET scan to ensure accurate results.
Looks like even your body’s viruses want to get in on the PET scan action, but they might just ruin the party.
Infections and PET Scan Results
PET scans may produce inaccurate results due to various medical conditions. One such condition is the presence of infections in the patient’s body as they can cause false-positive results on PET scans. These infections lead to higher glucose uptake in infected cells, which can be mistaken for tumour activity or inflammation.
Furthermore, certain types of infections like pneumonia and tuberculosis can affect the lungs’ glucose metabolism, affecting PET scan results significantly. Additionally, individuals with chronic inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus may have increased glucose metabolism in joints leading to false positives on PET scans.
It is crucial to inform your doctor about any existing medical conditions before taking a PET scan test as it helps avoid misinterpretation of results. Your doctor may reschedule the test, or offer treatment for an infection before proceeding with a PET scan.
Pro Tip: Always inform your healthcare provider about any pre-existing medical conditions, including infections or inflammatory diseases, before undergoing a PET scan for accurate results interpretation.
Before you jump into a PET scan machine, just remember: it’s not a carnival ride, it’s a medical procedure with cautions and limitations.
Cautions and Limitations of PET Scans
To be cautious while undergoing a PET scan, particularly for cancer detection, you need to consider a few limitations associated with it. With our section on ‘Cautions and Limitations of PET Scans’, we aim to acquaint you with the risks of PET scans and the limitations that occur in cancer detection. The subsections of this section, ‘Risks Associated with PET Scans’ and ‘Limitations of PET Scans in Cancer Detection,’ provide solutions to proceed with caution.
Risks Associated with PET Scans
When it comes to medical procedures like PET scans, there are a few things to be aware of. One area of concern is the potential risks associated with these scans. PET scans involve injecting a small amount of radioactive material into the body, which is used in conjunction with imaging technology to create detailed images of the internal organs and structures. These scans may pose some risks, including radiation exposure and allergic reactions.
In addition to these risks, it’s important to keep in mind the limitations of PET scans. While they can provide valuable information about certain conditions and illnesses, they may not always give a complete picture of what’s happening inside the body. For example, certain types of cancer may not be detectable on PET scans. It’s important to discuss the potential benefits and drawbacks of this procedure with your healthcare provider before undergoing a PET scan.
One unique aspect of PET scans is that they rely on radioactive material. This means that there are protocols in place to ensure that both patients and healthcare providers are safe during this procedure. Despite these measures, there have been instances where patients have been exposed to higher-than-normal amounts of radiation during their PET scan due to equipment malfunction or human error.
In one instance, a patient received 40% more radiation than was intended during her PET scan due to an equipment malfunction that went unnoticed by healthcare providers at the time. While she didn’t experience any immediate side effects as a result of this increased radiation exposure, she was advised to receive additional screening in the future.
When considering whether or not to undergo a PET scan, it’s important to weigh the potential risks and benefits with your healthcare provider and make an informed decision based on your individual health needs. Understanding the limitations and cautions associated with PET scans can help you feel comfortable and confident in your choice.
Cancer may be scary, but sometimes even PET scans need a break from searching for it.

Limitations of PET Scans in Cancer Detection
PET scans have limitations when it comes to detecting cancer. PET scans may not always pick up on small or early-stage tumours. Additionally, certain types of cancers might not show up well in PET Scans, such as prostate or brain cancer. PET scans can give false positives, leading to unnecessary anxiety and invasive procedures.
Furthermore, other conditions like infections may appear as cancerous areas on a scan. Comorbid disorders such as diabetes also cause an increased uptake of the radiotracer used in PET imaging, making images difficult to interpret.
One unique aspect is that patients who have undergone chemotherapy or radiation may experience inflammation and scarring that appears similar to cancer tissue on a scan. PET scanning also involves the use of radioactive materials that can be harmful if handled improperly.
Pro Tip: Discussing the risks and benefits of PET scans can aid in better decision-making for diagnosing cancer in patients with suspected cancers. Before you go scheduling a PET scan for every little ache and pain, remember: it’s better to be safe than PET-positive.